|
|
33-36 weeks
You and your baby at 33-36 weeks pregnant
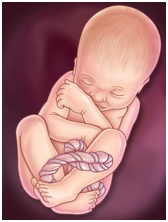 Your baby
By 33 weeks of pregnancy the baby’s brain and nervous system are fully developed. Your baby's bones are also starting to harden, even though the skull bones will stay soft and separated to make the journey through the birth canal (cervix and vagina) easier. Baby boys’ testicles are now beginning to descend from the abdomen into the scrotum.
You
You need to slow down because the extra weight will make you tired, and you may get backache.
From about 34 weeks pregnant, you may be aware of your womb tightening from time to time. These are practice contractions known as Braxton Hicks contractions, and are a normal part of pregnancy. It’s only when they become painful or frequent that you need to contact your midwife or hospital.
Only around 5% of babies arrive on their due date.
If you have children already, you may want to make childcare arrangements for when you go into labour. Pack your bag ready for the birth if you are planning to give birth in hospital.
When you are around 36 weeks pregnant, make sure you have all your important telephone numbers handy in case labour starts. Things to think about
Pain relief during labour
Be prepared by learning about all the ways you can relieve pain during labour so you can decide what’s best for you.
Make your birth plan
Think about your preferences for labour, for example pain relief and positions you might want to be in. You can save your birth plan online, or print out a blank form to fill in and discuss with your midwife.
If labour starts early
Labour that starts before 37 weeks is considered premature. If your baby is born early, he or she may need special care in hospital.
Warning signs during pregnancy
· Vaginal bleeding
Bleeding from your vagina may be a sign of a serious problem, so seek help.
· High blood pressure and pre-eclampsia
High blood pressure in pregnancy can be a sign of pre-eclampsia, which can be life-threatening if untreated.
· Severe itching
Severe itching can be a sign of the rare liver disorder obstetric cholestasis.
|





